Page 12 - The Indian EYE 072823
P. 12
OPINION JULY 28, 2023 | The Indian Eye 12
that sub-munitions can remain ex-
plosive hazards for decades. Cluster
munitions’ bomblets are generally
designed to explode or ignite upon
hitting the ground, but historically
their failure rate is the highest among
all classes of weapons, with lasting and
often devastating consequences for ci-
vilians. Civilian casualties are primar-
ily caused by munitions being fired
into areas where soldiers and civilians
are intermixed, inaccurate cluster mu-
nitions landing in populated areas, or
civilians traversing areas where clus-
ter munitions have been employed
but failed to explode.
Two technical characteristics of
submunitions—failure rate and lack
of a self-destruct capability—have
been at the core of the criticism of
cluster munition. There exist signifi-
cant discrepancies among failure rate
estimates. While a few manufactur-
ers claim a submunition failure rate
of 2 to 5 per cent, field reports have
recorded failure rates of 10 to 30 per
cent. Several factors influence submu-
nition reliability. In addition, factors
impacting higher failure rates of sub-
munition include delivery technique,
age of the submunition, air tempera-
ture, landing in soft or muddy ground,
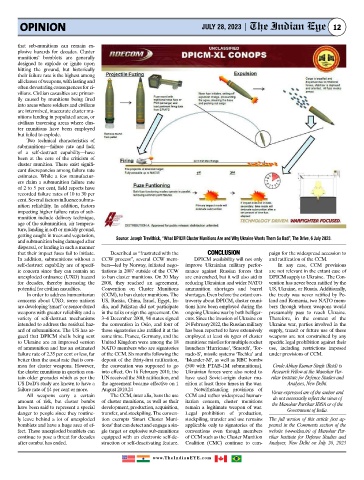
getting caught in trees and vegetation, Source: Joseph Trevithick, “What DPICM Cluster Munitions Are and Why Ukraine Wants Them So Bad”, The Drive, 6 July 2023.
and submunition being damaged after
dispersal, or landing in such a manner
that their impact fuses fail to initiate. Described as “frustrated with the CONCLUSION paign for the widespread accession to
In addition, submunitions without a CCW process”, several CCW mem- DPICM availability will not only and ratification of the CCM.
self-destruct capability are of specif- bers—led by Norway, initiated nego- improve Ukrainian military perfor- In any case, CCM provisions
ic concern since they can remain an tiations in 2007 outside of the CCW mance against Russian forces that are not relevant in the extant case of
unexploded ordnance (UXO) hazard to ban cluster munitions. On 30 May are entrenched, but it will also aid in DPICM supply to Ukraine. The Con-
for decades, thereby increasing the 2008, they reached an agreement, reducing Ukrainian and wider NATO vention has never been ratified by the
potential for civilian casualties. Convention on Cluster Munitions ammunition shortages and barrel US, Ukraine, or Russia. Additionally,
In order to address humanitarian (CCM), to ban cluster munitions. The shortages. Even before the extant con- the treaty was never ratified by Po-
concerns about UXO, some nations US, Russia, China, Israel, Egypt, In- troversy about DPICM, cluster muni- land and Romania, two NATO mem-
are developing ‘smart’ or sensor-fuzed dia, and Pakistan did not participate tions have been employed during the bers through whom weapons would
weapons with greater reliability and a in the talks or sign the agreement. On ongoing Ukraine war by both belliger- presumably pass to reach Ukraine.
variety of self-destruct mechanisms 3–4 December 2008, 94 states signed ents. Since the invasion of Ukraine on Therefore, in the context of the
intended to address the residual haz- the convention in Oslo, and four of 24 February 2022, the Russian military Ukraine war, parties involved in the
ard of submunitions. The US has ar- those signatories also ratified it at the has been reported to have extensively supply, transit or future use of these
gued that DPICM shells being sent same time. France, Germany, and the employed at least six types of cluster weapons are not constrained by any
to Ukraine are an improved version United Kingdom were among the 18 munitions: missiles for multiple rocket specific legal prohibition against their
of ammunition and has an estimated NATO members who are signatories launchers ‘Hurricane’, ‘Smerch’, ‘Tor- use, including restrictions imposed
failure rate of 2.35 per cent or less, far of the CCM. Six months following the nado-S’, missile systems ‘Tochka’ and under provisions of CCM.
better than the usual rate that is com- deposit of the thirty-first ratification, ‘Iskander-M’, as well as RBC bombs
mon for cluster weapons. However, the convention was supposed to go (500 with PTAB-1M submunitions). Cmde Abhay Kumar Singh (Retd) is
the cluster munitions in question con- into effect. On 16 February 2010, the Ukrainian forces were also noted to Research Fellow at the Manohar Par-
tain older grenades which as per the UN received the 30th ratification, and have used Soviet-origin cluster mu- rikar Institute for Defence Studies and
US DoD’s study are known to have a the agreement became effective on 1 nition at least three times in the war. Analyses, New Delhi.
failure rate of 14 per cent or more. August 2010.24 Notwithstanding provisions of Views expressed are of the author and
All weapons carry a certain The CCM, inter alia, bans the use CCM and rather widespread human-
do not necessarily reflect the views of
amount of risk, but cluster bombs of cluster munitions, as well as their itarian concern, cluster munitions the Manohar Parrikar IDSA or of the
have been said to represent a special development, production, acquisition, remain a legitimate weapon of war. Government of India.
danger to people since they routine- transfer, and stockpiling. The conven- Legal prohibition of production,
ly leave behind a lot of unexploded tion exempts ‘Smart Cluster Muni- stockpiling, transfer and use remains The full version of this article first ap-
bomblets and have a huge area of ef- tions’ that can detect and engage a sin- applicable only to signatories of the peared in the Comments section of the
fect. These unexploded bomblets can gle target or explosive sub-munitions conventions even though members website (www.idsa.in) of Manohar Par-
continue to pose a threat for decades equipped with an electronic self-de- of CCM such as the Cluster Munition rikar Institute for Defense Studies and
after combat has ended. struction or self-deactivating feature. Coalition (CMC) continue to cam- Analyses, New Delhi on July 20, 2023
www.TheIndianEYE.com